Like
I said earlier in part 1 of this chapter,
there are queries that are better built or designed through MS Access query wizards. The
main 3 queries that I will advise you to build through the query wizards are:
1. Find Duplicates Query
2. Find Unmatched Query
3. Crosstab Query
You
can also build these 3 queries through the query design but it will be very
tedious. Also it is very difficult to debug their errors. But the Microsoft
Access Query wizard simplifies the design steps for you and also reduces the
possible errors.
You
can also build simple select query through the query wizard, but building it
through query design gives you more flexibility because it allows you to
construct everything from the scratch.
Other
queries like the four action queries (make table, update, append and delete
queries), parameter queries are better and easier to build through query
design.
I
will now show you how you can utilize MS Access query wizard to easily build
the Find Duplicates query, Find Unmatched query and Crosstab query. In part 1, I explained action queries in
detail.
FIND DUPLICATES QUERY
This
type of advanced query helps you find records with duplicate field values in a
single table or a previously created query. When using MS Access query wizard
to create the find duplicates records query, you will be required to specify
the field or column on which the query filter process will be based i.e. the
field that could contain the duplicate field values.
For
example, a university registrar may want to filter out the records of students
that will graduate in a particular date or the dates where more than one
student will graduate. In either cases, he will specify the REG DATE field in
the query wizard as the field that will contain the duplicate values.
To Build the Find Duplicates Query through MS Access Query Wizard:
1. Click the Create
tab and then click the Query Wizard
icon located in the Queries group.
2. This prompts the New Query Wizard
dialogue box. Select Find Duplicates Query Wizard, then click OK as shown below.
3. Next, select the table that may contain duplicate values. Referring to
the above example, the name of the table is Students Record, then click Next.
4. Select the field(s) that may contain duplicate field values or information. Also referring to the above
example, I will select the REG DATE field because it is the field that has the
duplicate registration date values.
5. With that field selected, click the single forward pointing arrow button
(>) to move the selected field from Available
fields to Duplicate-value fields,
then click Next as shown below.
6. Select the other fields that you would like the find duplicates query to
display in addition to the duplicate value fields you selected earlier. You can
select all the remaining fields if you wish. Then click Next as shown below.
7. Type a unique name for the query, Specify whether to view the query or
modify the query design further, then click Finish as shown below.
8. MS Access runs the query and displays the records for you. Check whether
the find duplicates query returned the desired result, then close the query.
FIND UNMATCHED QUERY
This type of advanced
query helps you find records in one table that have no related records in
another table. The Find Unmatched Records query compares the two table and
filters the records that have no related record in the order table. This means
that both tables must have a matching field in which MS Access will base its
comparison and filter process in the query wizard.
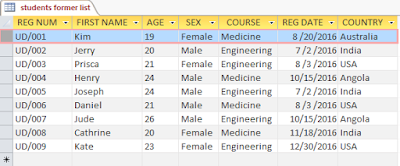
For example, a
university registrar has been making use of two similar tables namely: Students Former List and Students Recent List to store the
records of new students and he knows that the records of some set of students
are contained in both tables. If he wants to filter or extract the records of
the other students that are not duplicated in the two tables, then he must use
the Find Unmatched Query. The two tables are shown below.
The 2 tables have the same structure. Now, studying the two
tables closely, which field do you think could best serve as the matching field?
Answer: The REG
NUM field of course. This is because 2 different students other information may
coincide, but the registration number can never be the same
To Build the Find Unmatched Query through MS Access Query Wizard:
1. Click the Create
tab and then click the Query Wizard
icon located in the Queries group.
2. This prompts the New Query Wizard
dialogue box. Select Find Unmatched
Query Wizard, then click OK
as shown below.
3. Next, the find unmatched query wizard asks you to specify
the first table or query that contains records you want in the query results.
You can specify any of the tables first. So referring to the example above, I
will select the Students Former List table.
Click Next as shown below.
4. Next, you specify the other table or query that contains the
related records. In my case, I will now select the Students Current List table. Click Next as shown below.
5. Now you have to specify the matching fields in both table.
These fields must have the same data type and must contain similar or related
data or information. Referring to the above example, the matching field is the
REG DATE field, so I will select this field in both table. Click the Matching fields button in between the
two tables, then click Next as shown
below.
6. Next, select the other fields you would like to see in the
find unmatched records query results and click Next.
7. Type a unique name for your new find unmatched records query.
Specify if you would like view the query results or to modify it further in the
query design view. Then Click Finish
as shown below.
8. MS Access now runs the query and displays the records that
do not match in both tables as shown below. Cross check the query results to
see if it returned the desired records. Then close the query.
CROSSTAB QUERY
This type of action query is used to calculate and restructure data for easier analysis. Crosstab query can be used to calculate a SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT or other types of total functions
for data that are grouped by two types of information. When
using the crosstab query, you have to specify the Row Heading field(s), the Column
Heading field and the Calculation field.
The crosstab query is very similar to the select query.
This means that some of the thing achieved with a crosstab query can also be
achieved with the simple select query, but the crosstab query simplifies the
returned results further for easier data analysis.
For example a Manager of an organization may like to
analyze his workers payroll system to see the total amount spent. He may like
to analyze the data based on two categories: the total amount spent on each
marital status category (i.e. married and single workers) and total amount
spent on each qualifications category. His company employs based on these four
qualifications: PhD, MSc, BSc and HND. A sample of
the company’s workers’ payroll system is shown below.
To achieve his desired analysis, he will use a crosstab
query. During the design, he will specify the M STATUS field as the Row Heading field, then the QUAL field
will be the Column Heading field.
Lastly, he will specify the BASIC SALARY field as his Calculation field.
You can create a crosstab either through the Design Query or through the Query Wizard. But it is easier and
less stressful when built through the Query wizard.
To Build the Crosstab Query through MS Access Query Wizard:
1. Click the Create
tab and then click the Query Wizard
icon located in the Queries group.
2. This prompts the New Query Wizard
dialogue box. Select Find Unmatched
Query Wizard, then click OK
as shown below.
3. Next, you specify the data source (table or query) that
contains the fields you want to use for the crosstab query results. Referring
to the above example, the name of the payroll table is Workers Payroll System. Click Next
as shown below.
NOTE:
If the fields you want to use for your crosstab query are
contained in two different tables or queries, then you have to first create a
select query to filter all the fields you need before you continue with the
crosstab query.
4. Now, select the field(s) you want to use as Row Headings, click the
forward-pointing arrow button to transfer the selected fields from the Available Fields box to the Selected Fields box one after the
other. From the example above, the Row
Heading field is the M STATUS field. Click Next as shown below.
5. Next, select the field you want to use as Column Headings. You can only select
one field here. From the example above, the Column Heading field is the QUAL field. Click Next as shown below.
6. Specify the Calculation
field and also specify the Function
you want the wizard to use in the selected field. From the above example, the
calculation field is the BASIC SALARY field and the function to apply in this
field is the SUM function because the Manager want to know the total amount
spent in each category. Also specify if you want to include row sum by checking
the Yes, include row sum check box.
Then click Next as shown below.
7. Type a unique name for your new crosstab query. Also specify
if you would like view the query results or to modify it further in the query
design view. Then Click Finish.
8. MS Access now runs the query and summarizes the records in
that table as shown below. Cross check the query results to see if it returned
the desired records. Then close the query.
So
these are the 3 main types advanced queries you can easily build with the MS
Access Query wizard.
Now in part 3 (the
last part of this chapter), I will explain Parameter Query (the most versatile
and easiest type of advanced query) in detail.
Inform your friends about this post by clicking the share button below. Comment below if you are hooked up along the installation process.
Also click Here to subscribe for free so that you will get our latest game updates in your email.



































No comments:
Post a Comment
WHAT'S ON YOUR MIND?
WE LOVE TO HEAR FROM YOU!